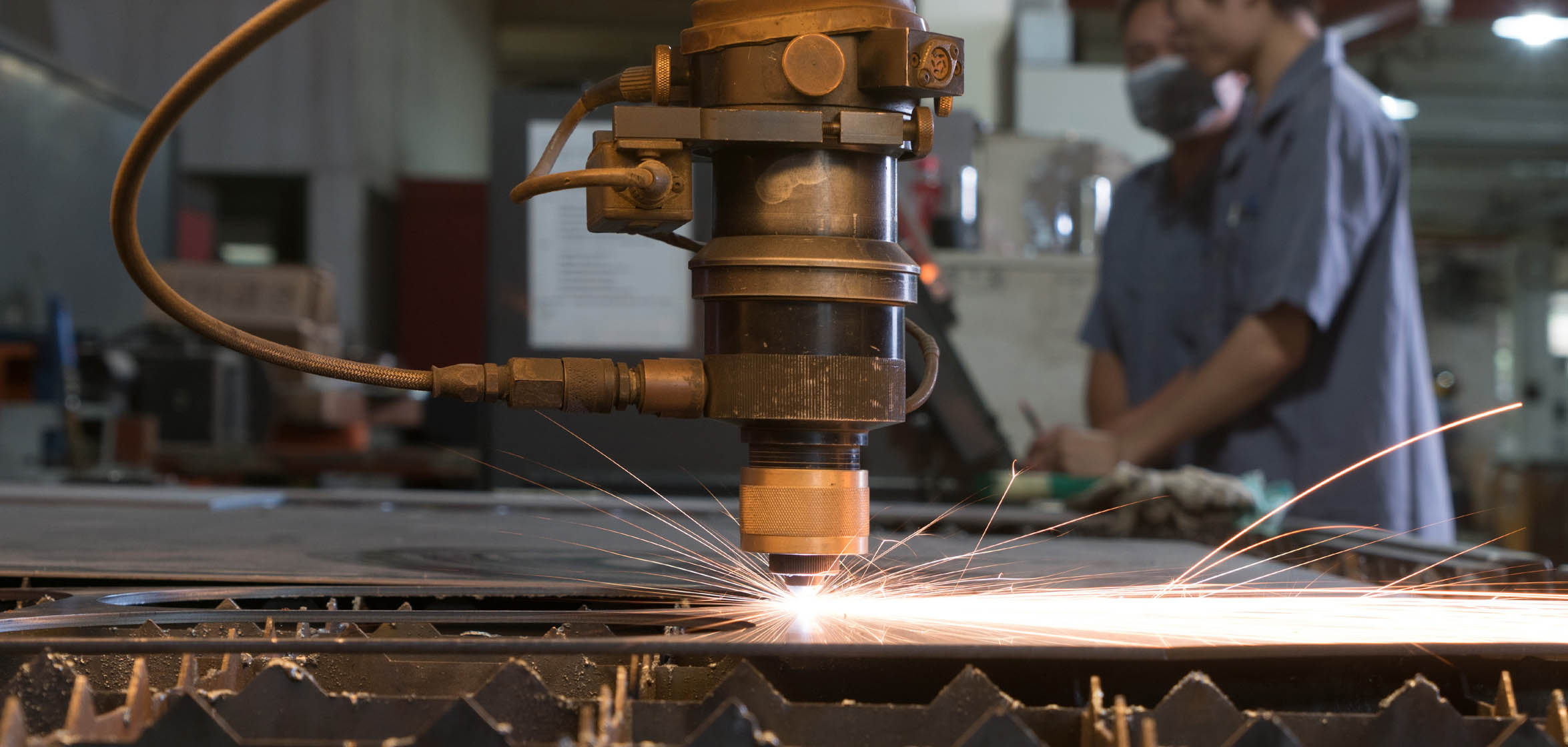
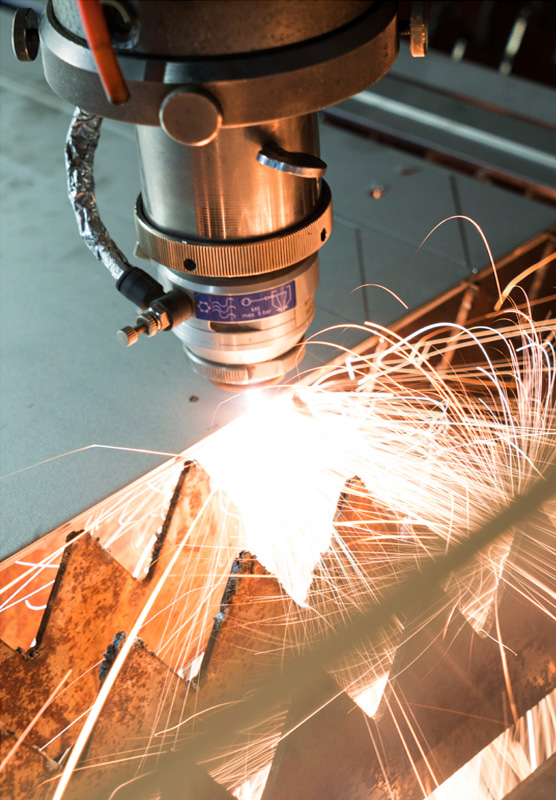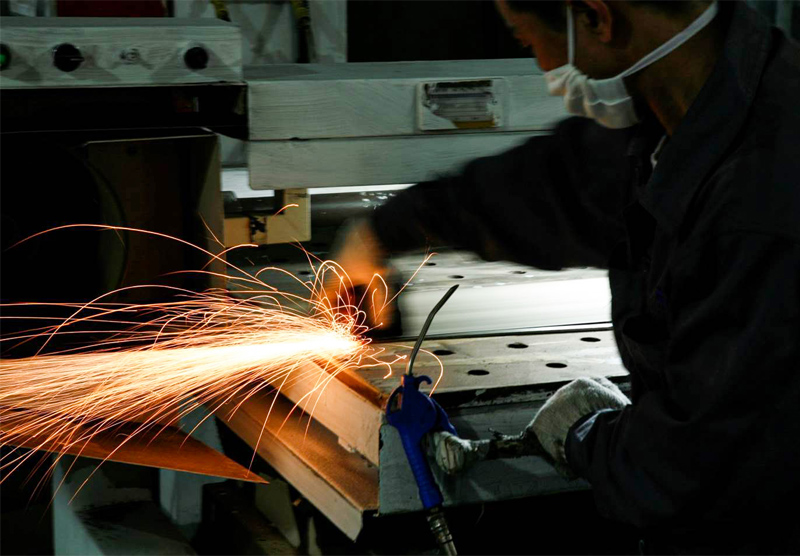
Cutting is a collection of processes wherein material is brought to a specified geometry by removing excess material using various kinds of tooling to leave a finished part that meets specifications. The net result of cutting is two products, the waste or excess material, and the finished part. In woodworking, the waste would be sawdust and excess wood. In cutting metals the waste is chips or swarf and excess metal.
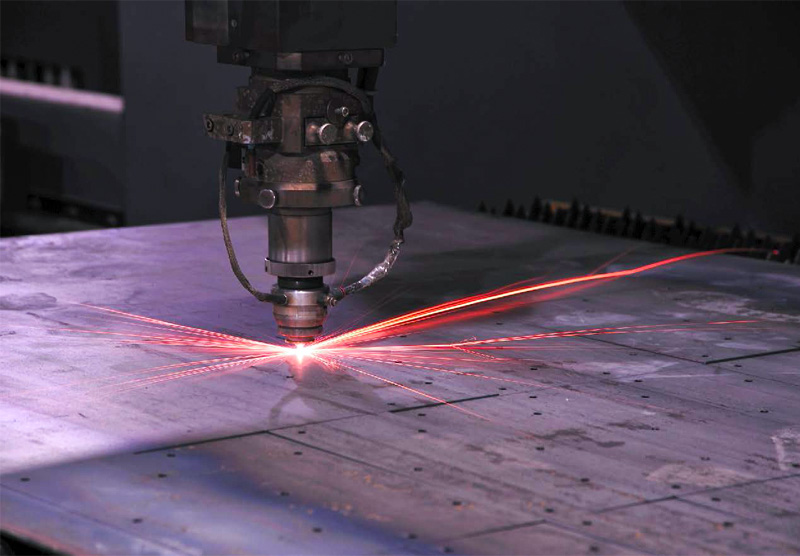
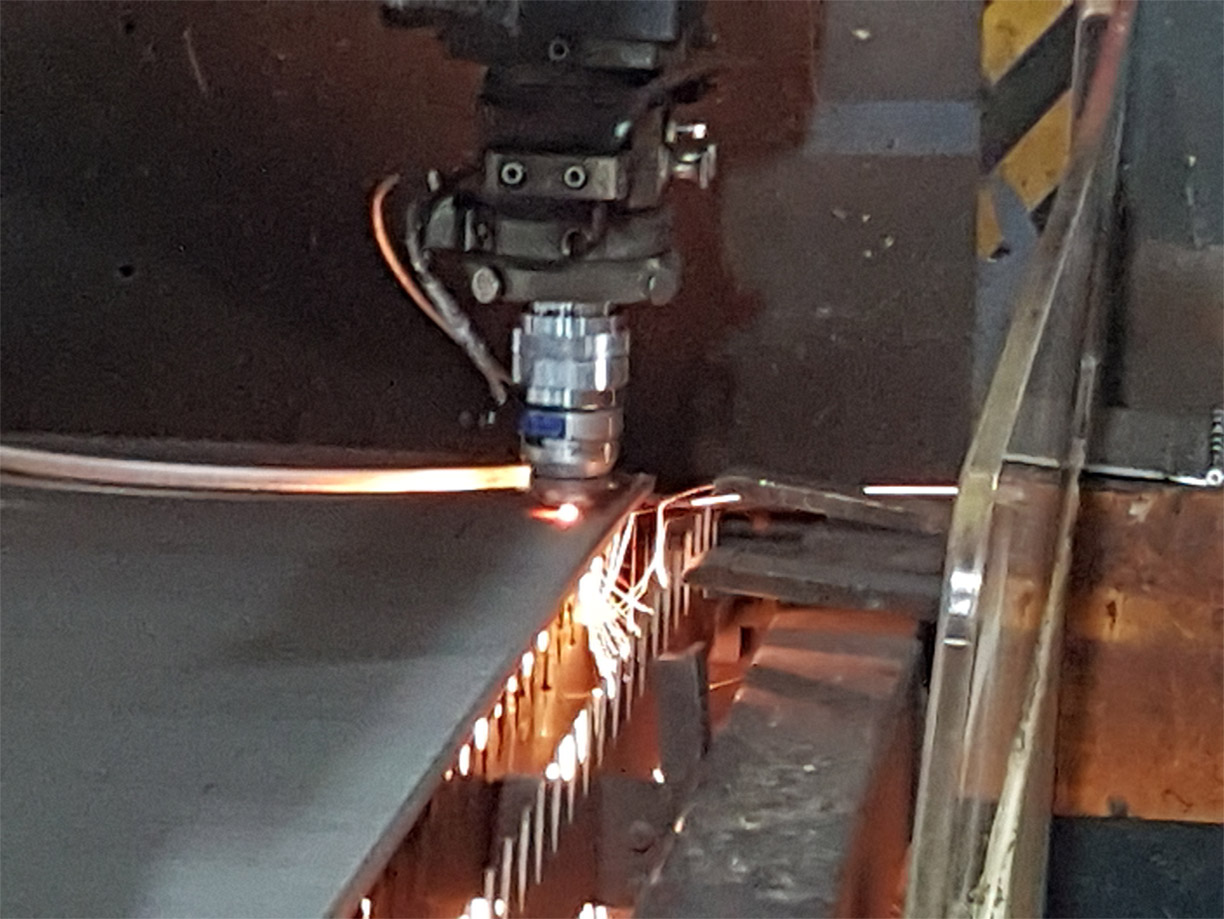
With laser cutting, a highly concentrated beam of light reaches an extremely high temperature. This hot beam can cut metal precisely and efficiently. When used in conjunction with the latest computer programs, the laser can be controlled with a high level of accuracy, giving a neat finish and enabling intricate designs to be followed.
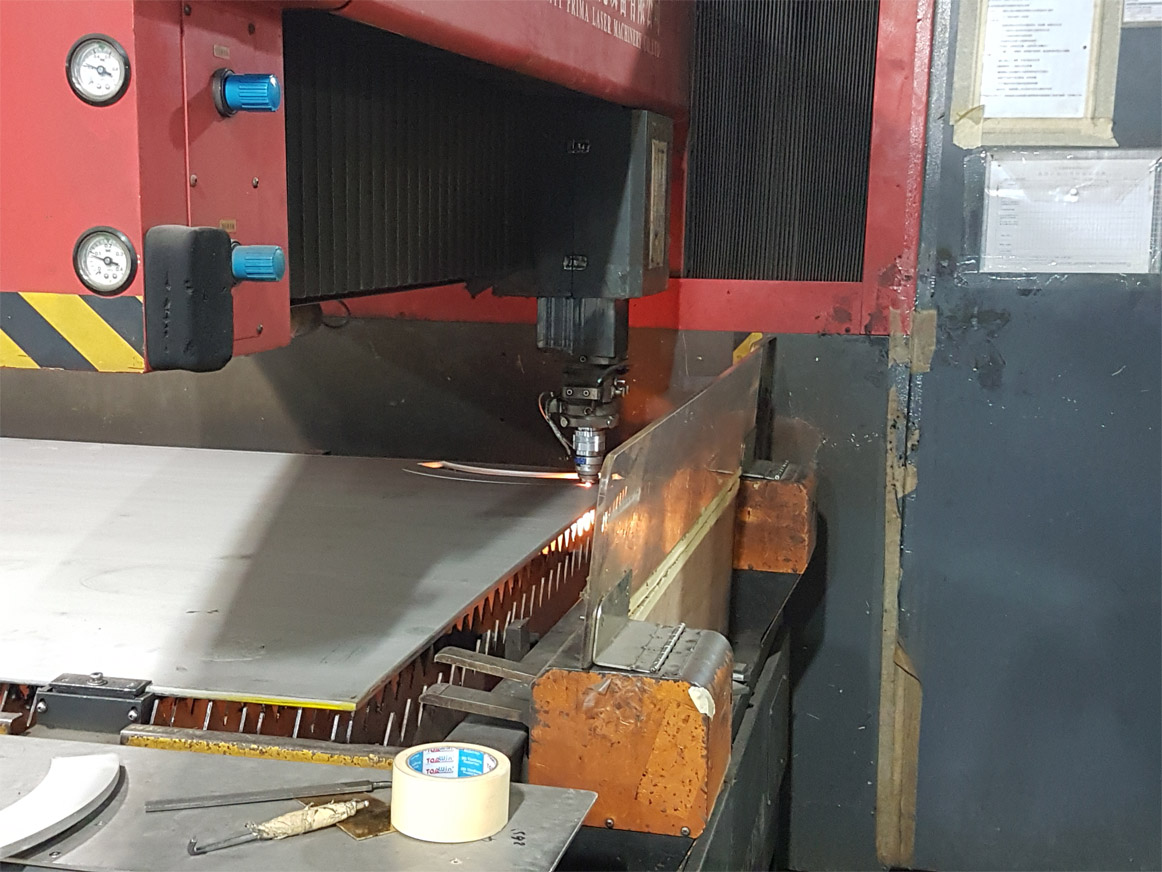
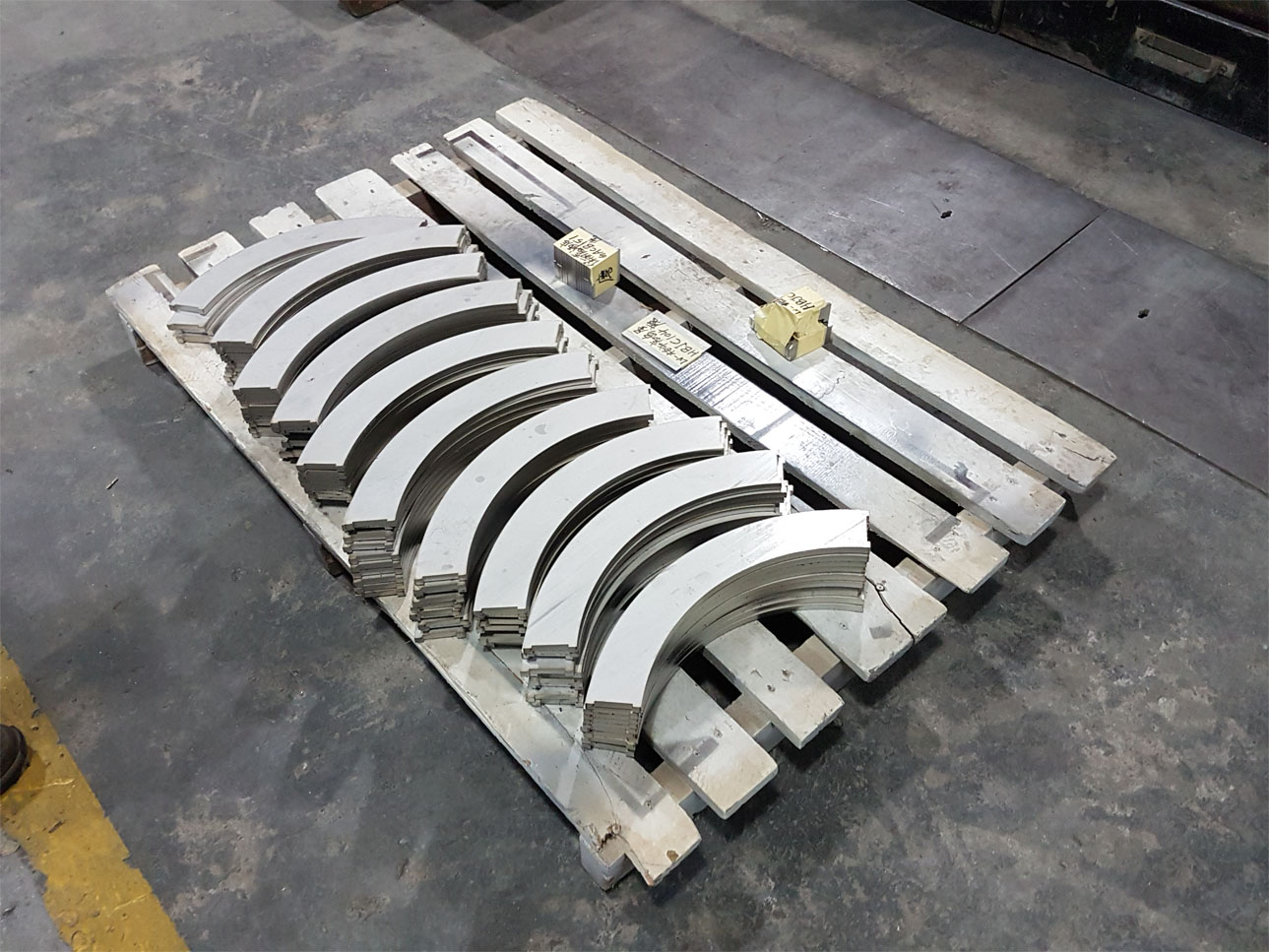


Drilling a hole in a metal part is the most common example of a chip producing process. Using an oxy-fuel cutting torch to separate a plate of steel into smaller pieces is an example of burning. Chemical milling is an example of a specialty process that removes excess material by the use of etching chemicals and masking chemicals.

